Correlation between bone mineral densitometry and liver/heart iron overload evaluated by quantitative T2* MRI
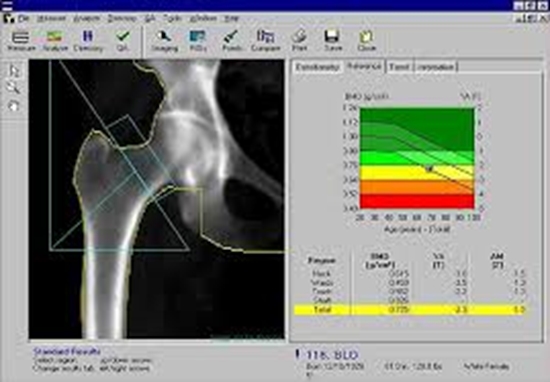
Background:Osteomalacia and osteoporosis are a common clinical problem in patients with betathalassemia major. The purpose of this study is to assess the possible correlation of excess iron in liverand heart of beta thalassemia patient with bone mineral density (BMD).Materials and methods:We performed a prospective cross-sectional study on 80 patients with betathalassemia major and inermedia. The patients were stratified into normal BMD and those with abnormalBMD test based on T-score. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging examinations of heartand liver. Multi-echo fast gradient-echo sequence was used and T2* values were calculated based on theRoyal Brompton Hospital protocol. Correlations between T2* values in heart and liver as well as serumferritin levels with femoral and lumbar BMD were investigated.Results:There were no significant differences between patients with and without osteopenia or osteoporosiswith respect to age and sex. Patients with abnormal BMD had lower T2* values in the heart. Serum ferritin andheart iron load (based on T2*) were negatively correlated with BMD.Conclusion:Serum ferritin and heart iron content are good indicators of BMD in patients with betathalassemia major and intermedia




ارسال نظر