Unveiling the Uncommon: Gas-Containing Renal Stones - A Unique Case Study
INTRODUCTION
Gas-containing renal stones, documented in only 12 cases before this,1 remain a medical rarity, often associated with recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs).2 This contribution sheds light on the thirteenth reported case, exploring clinical nuances, imaging nuances, and tailored management approaches.
2 CASE PRESENTATION
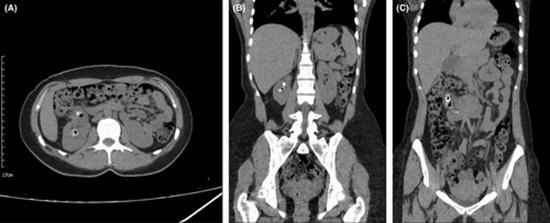
A 31-year-old woman with a history of three times UTIs, who has undergone two times percutaneous nephrolithotomies (PCNL) and one transurethral lithotomy (TUL) due to previous renal stones, and without a history of diabetes mellitus, vesicourethral reflux or hypertension, came at the emergency department with right flank pain and macroscopic hematuria. Plain computed tomography (CT) revealed numerous stones containing gas in all calyces and pelvis with maximum dimensions of 22 × 14 mm in the right kidney accompanied by horseshoe kidneys (Figures 1A–C and 2). Urine analysis also showed a significant white blood cell count, and moderate bacteria and urine culture results showed Escherichia coli growth.



ارسال نظر