Diagnostic Accuracy of Sixty Four Multi-Slice CT Angiography in Assessment of Arterial Cut-Off and Run-Off in Comparison with Surgical Findings
We aimed to determine the diagnostic value of 64-multislice CT angiography (MSCTA) in run-off and cut-off sites of arterial disease.
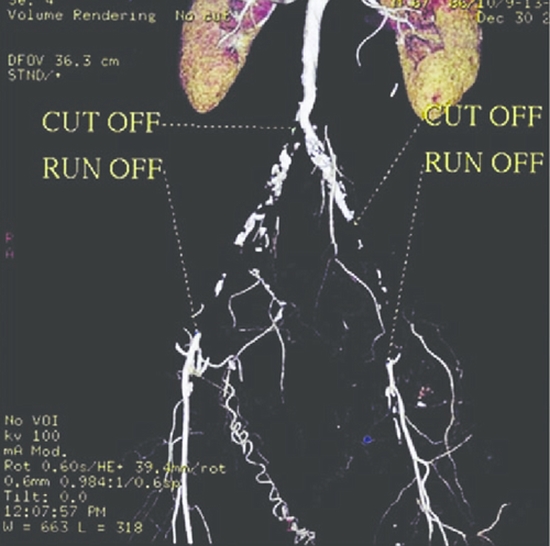
Background/objective: The accurate anatomic mapping and determination of the severity of arterial disease, an important health problem of the elderly, is of great significance. We aimed to determine the diagnostic value of 64-multislice CT angiography (MSCTA) in run-off and cut-off sites of arterial disease.
Patients and methods: Throughout the study, MSCTA followed by an operative intervention was carried out on a total of 38 patients with clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of arterial disease (AD) all of whom had the indication for vascular surgery. The mean age of patients was 34±15.86 (range, 23 to 93) years. MSCTA was executed using a 64-slice CT scanner, during the arterial phase of injecting the nonionic, contrast medium with a power injector at the rate of 5 ml/sec into the antecubital vein and exploration and revascularization of peripheral arterial disease was performed intraoperatively.
Results: Atherosclerosis and arterial disease, the most common causes of vascular occlusion, were more common in the lower extremities. According to MSCTA findings, the most frequent site of stenosis was the superficial femoral artery. Spearman's correlation coefficient showed a high degree of agreement amongst the raters. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and the accuracy of MSCTA compared to surgery were 83.8%, 96%, 96.8%, 81.3% and 89%, respectively. MSCTA findings were compared with surgery as a standard of reference, which showed concordance in the majority of cases (81.6%). Cut-off sites were correctly identified by MSCTA in 97.3% of the patients and the most common sites of discordance were the run-off sites (18.2%).
Conclusion: MSCTA angiography as a novel diagnostic modality may be a suitable alternative and a viable choice for routine clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: Arterial Disease; Cut-Off; Diagnostic Accuracy; Run-Off Site; Sixty Four Multi-Slice CT Angiography; Surgery.






Send to friends