Management of Liver Hemangioma Using Trans-Catheter Arterial Embolization
Hemangioma, a congenital vascular malformation, is the most common benign liver lesion that is usually remain stable subsequently requiring not treatment; however, complications such as abdominal pain or fullness, coagulation disturbances, and inflammatory syndrome may occur, demanding a specific treatment of hemangioma.
Background:
Hemangioma, a congenital vascular malformation, is the most common benign liver lesion that is usually remain stable subsequently requiring not treatment; however, complications such as abdominal pain or fullness, coagulation disturbances, and inflammatory syndrome may occur, demanding a specific treatment of hemangioma.
Objectives:
To assess the safety, feasibility and efficacy of trans-catheter arterial embolization (TAE) for the treatment of Liver hemangioma
Patients and Methods:
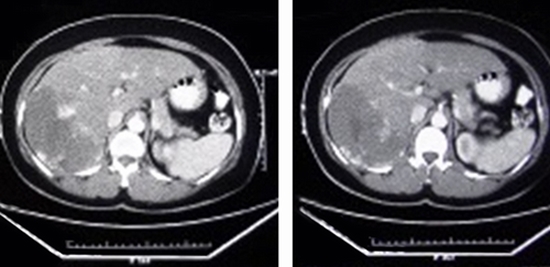
TAE was performed on 20 patients with liver hemangioma. The embolic agent used was polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles (300-400 micron, Jonson and Johnson Cordis, USA). All patients were followed up for 6 months. Imaging was carried out and patients were also evaluated symptomatically through telephone interview by a physician.
Results:
Twenty patients aged from 21 to 63 years (mean: 46.8, SD: 10.26) were included in this study. Post embolization syndrome, including abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis occurred in one patient 1 week after TAE and lasted for 3 days. No serious adverse event and TAE-related death was observed. None of the patient underwent another intervention including surgery. During follow up interval, decreased episode of abdominal pain was documented in all patients who had pain. Tumor enlargement was also stopped during the follow up. The average diameter of tumors was 97.00 mm (range: 25-200 SD: 47.85) and 88.95 mm (range: 23-195 SD: 43.27) before and after embolization, respectively. Comparison of images before and after TAE revealed statistically significant decrease in the size of lesion (P value: 0.004, t: 3.31).
Conclusions:
Our findings indicate that TAE is a safe and efficient procedure for the treatment of liver hemangioma. Further studies with larger sample sizes are required to support therapeutic effects of TAE.






Send to friends