Neonatal Outcomes of Fetuses with Isolated or Multiple Soft Markers in Ultrasound Screening
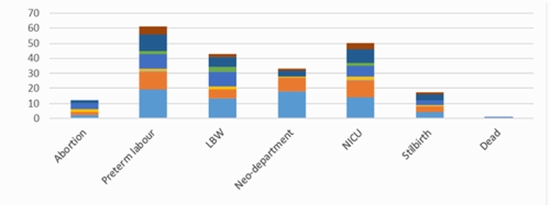
Background: There is still controversy on the importance of soft markers on the fetus and neonatal outcomes. This study aimed to determine the mentioned outcomes in the fetuses with soft markers detected by ultrasound screening. Methods: This prospective study was conducted on 461 pregnant women who were referred to the prenatal clinics of hospitals affiliated with the Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, in 2021. The study outcomes included incidence of abortion, preterm birth (PTB), cesarean section (CS), low birth weight (LBW), neonatal admission rates, and neonatal mortality. Results: The most frequent soft marker in the present study was echogenic intra-cardiac foci (EIF) (32.5%), followed by choroid plexus cyst (CPC) (30.6%), pyelectasis (25.2%), and echogenic bowel (EB) (15.8%), respectively. Spontaneous abortion, PTB, CS, LBW, neonatal department admission, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admission, stillbirth, and fetal distress, and death occurred in 10 (2.1%), 52 (12.5%), 316 (76%), 35 (7.6%), 28 (6.7%), 42 (10.1%), 13 (3.1%), 26 (5.6%), and one (0.24%) cases, respectively. Poor neonatal outcomes were significantly associated with EIF (P=0.007), CPC (P=0.045), echogenic bowel (P=0.031), pyelectasis (P=0.026), and single umbilical artery (P=0.010). In addition, the fetuses with synchronous CPC and IEF and also synchronous pyelectasis and IEF were at significantly higher risk of poor neonatal outcomes (P=0.037). Conclusion: The study results showed that although poor neonatal outcomes were associated with some soft markers, most fetuses with soft markers had desired outcomes in the absence of structural or chromosomal abnormality






comment