Neurochemical Alterations Linked to Persistent COVID 19 Induced Anosmia: Probing Into Orbitofrontal Cortex by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
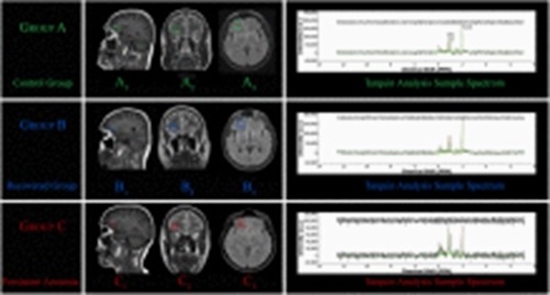
Background: While many COVID-19-induced anosmia patients recover their sense of smell within a few months, a substantial number of them continue to experience olfactory impairment. In our primary study, the metabolic patterns in orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) were observed to exhibit more alterations than other regions. Hence, this study specifically probes into alterations within OFC region in subjects with persistent COVID-19-induced anosmia.
Methods: In a new categorization, 54 subjects were studied as two major groups of COVID-19-related anosmia and normal each of which includes 27 subjects. Iran Recognition-Smell Identification Test (IR-SIT) over a three-month follow-up period was utilized for olfactory function assessment and anosmia diagnosis. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-MRS) was employed to examine changes of metabolites in OFC, including N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), choline (Cho), and creatine (Cr), as well as their ratios. Additionally, a linear regression was applied to investigate the potential correlation between MRS data and IR-SIT scores.
Results: Patients with COVID-19-induced anosmia exhibited a significant reduction in NAA, Cho, and Cr levels in the OFC region compared to the control group. Moreover, NAA/Cho and NAA/Cr ratios were lower in the anosmia patients, whereas the Cho/Cr ratio elevated. The NAA/Cho ratio had the highest linear correlation with IR-SIT scores in anosmia.
Conclusion: This study highlights remarkable neurochemical patterns associated with COVID-19-induced anosmia in brain orbitofrontal cortex detectable by proton MRS, shedding light on the link between OFC function impairment and anosmia. The NAA/Cho ratio derived from MRS data emerged as a potential biomarker that correlates with anosmia severity and recovery examination.






comment