Outcome of Retinoblastoma Following Limited Sessions of Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy in Iran
The management of retinoblastoma remains a challenge to the multidisciplinary team, particularly as treatment affects not only visual outcomes, but also ocular retention and morbidity. Management of retinoblastoma has evolved over the past two decades
Background:
The management of retinoblastoma remains a challenge to the multidisciplinary team, particularly as treatment affects not only visual outcomes, but also ocular retention and morbidity. Management of retinoblastoma has evolved over the past two decades.
Objectives:
To report the result of intra-ophthalmic artery chemotherapy (IAC) for the treatment of refractory and advanced retinoblastoma tumors.
Patients and Methods:
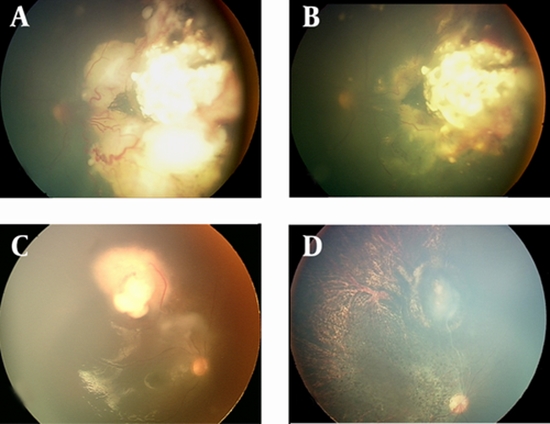
All patients who had failed to respond adequately to previous treatments and six naive patients with advanced retinoblastoma, receiving IAC between 2009 and 2012, were included in this institutional interventional case series. The patients received 1-2 treatments of IAC given 4-8 weeks apart. Complete response was defined as regressed tumor and complete disappearance of seeding clinically and partial response was defined as partial regression of the tumor with live parts of the tumor and/or lessening of seeds, but not complete disappearance of them clinically.
Results:
A total of 24 eyes of 24 patients were treated with IAC during the study period. The mean age at the time of IAC was 38.9 months (14-120 months), and the mean follow-up was 16.8 months (3-36 months) after IAC. Tumor control was achieved in 14 eyes (58.3%). Type 3 (combined fleshy and calcified remnants) was the most common type of regression (37.5%). Complications included vitreous hemorrhage in nine eyes (37.5%), arterial occlusion in two (8.3%), cyclitic membrane possibly secondary to ischemia and tractional retinal detachment in one patient (4.2%), chorioretinal atrophy in three (12.5%) patients, and neovascular glaucoma in one eye (4.2%). In eight (33.3%) patients, no complication happened. Globe salvage was achieved in 62.5% of the cases. The success rate for naive patients was 84%. Sixty-seven percent of the cases received transpupillary thermotherapy and cryotherapy before IAC.
Conclusions:
Intra-ophthalmic artery melphalan is an effective treatment for advanced cases of retinoblastoma, with a reasonable level of success. In the short follow up period of this study, it appears that the primary cases showed better results in the control of tumor






Send to friends