The value of bronchocele attenuation in pulmonary computed tomography in assessment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in the background of cystic fibrosis: A cross sectional study
Background: There is no specific test in the definitive diagnostic approach to Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) especially in the background of cystic fibrosis, but comprehensive and simultaneous clinical, radiological and serological examination will be the basis of ABPA diagnosis. The increasing in attenuation of bronchoceles in imaging has recently been proposed as a valuable diagnostic criterion.
Purpose: The present study aimed to assess bronchocele attenuation in pulmonary CT scan of patients with complicated cystic fibrosis for diagnosis of ABPA.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was performed on 74 consecutive patients aged 3-18 years suffering cystic fibrosis presented with exacerbation of pulmonary symptoms and were suspected of having ABPA. All were examined by 16 Slice CT Scan and the density of bronchoceles above 5 mm in diameter were measured in Hounsfield unit. The total serum IgE titer, skin prick test for aspergillus and anti-aspergillus IgG and IgE level were obtained for all subjects and both cutoff values of IgE level (>500 IU/mL and >1000 IU/mL) were considered as the criteria for ABPA diagnosis.
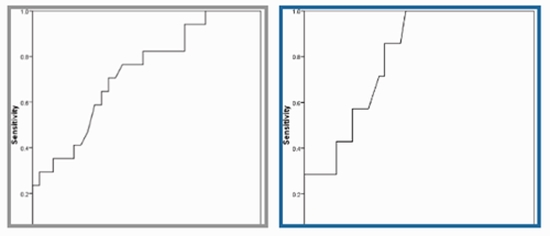
Results: Considering IgE level of greater than 500 IU/mL and 1000 IU/mL as the diagnostic criteria, 24.3% and 10.8% had evidence of ABPA, respectively. Considering the two pointed diagnostic IgE ranges and based on the analysis of the area under the ROC curve, bronchocele attenuation could effectively predict the presence of ABPA with the best cutoff values of 37.25 (with a sensitivity of 70.6% and a specificity of 66.7%) and 40.00 (with a sensitivity of 85.7% and a specificity of 65.1%), respectively.
Conclusion: The presence of bronchocele and an increase in its attenuation on CT scan will be diagnostic for the occurrence of ABPA.






comment