Y The Effect of Contrast Enhanced Abdominopelvic Magnetic Resonance Imaging on Expression and Methylation
Objective
To evaluate the effect of contrast enhanced abdominopelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), using a 3 Tesla scanner, on expression and methylation level of ATM and AKT genes in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Materials and Methods
In this prospective in vivo study, blood samples were obtained from 20 volunteer patients with mean age of 43 ± 8 years (range 32-68 years) before contrast enhanced MRI, 2 hours and 24 hours after contrast enhanced abdominopelvic 3 Tesla MRI. After separation of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood, using Ficoll-Hypaque, we analyzed gene expression changes of ATM and AKT genes 2 hours and 24 hours after MRI using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). We also evaluated methylation percentage of the above mentioned genes in before, 2 hours and 24 hours after MRI, using MethySYBR method.
Results
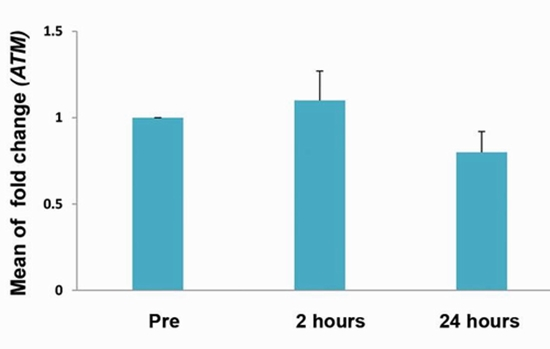
Fold change analysis, in comparison with the baseline, respectively showed 1.1 ± 0.7 and 0.8 ± 0.5 mean of gene expressions in 2 and 24 hours after MRI for ATM, while the results were 1.4 ± 0.6 and 1.4 ± 1 for AKT (P>0.05). Methylation of the ATM gene promoter were 8.8 ± 1.5%, 9 ± 0.6% and 9 ± 0.8% in before contrast enhanced MRI, 2 and 24 hours after contrast enhanced MRI, respectively (P>0.05). Methylation of AKT gene promoter in before contrast enhanced MRI, 2 hours and 24 hours after contrast enhanced MRI was 5.4 ± 2.5, 5 ± 3.2, 4.9 ± 2.9 respectively (P>0.05).
Conclusion
Contrast enhanced abdominopelvic MRI using 3 Tesla scanner apparently has no negative effect on the expression and promoter methylation level of ATM and AKT genes involved in the repair pathways of genome.






Send to friends