CT Scan Guided Intra-orbital Amphotericin Injection in COVID19 associated Mucormycosis, a pilot study
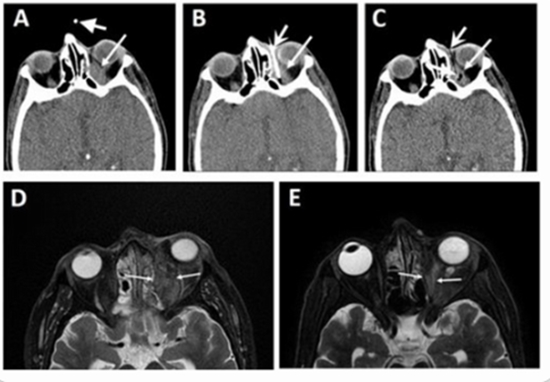
Purpose : A high incidence of sinu-orbital Mucormycosis as a fulminant and opportunistic fungal infection happened following the COVID-19 pandemic. Traditionally, patients with apical or extensive orbital involvement are candidates for exenteration. We designed and applied CT scan guided orbital amphotericin C delivery. In this study we aimed to report this novel technique and results of this method in control of orbital mucormycosis with apical involvement.
Methods : A high incidence of sinu-orbital Mucormycosis as a fulminant and opportunistic fungal infection happened following the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus named as CAM. Traditionally, patients with orbital mucormycosis with apical or extensive involvement are considered hopeless for saving the eye. We designed and applied CT scan guided orbital amphotericin C delivery.
Results : A total of thirty patients with mean age of 52±11.86 were enrolled in this study. Twenty-three (76.7%) patients were male; group A: 11 (73.3%) and B: 12 (80%). The majority of the patients in both group were diabetics (A: 10 (66.7%), B: 10 (76.9%)). Most patients in both groups had received corticosteroids and antiviral therapy for their recent COVID-19, 23 (82.1%) and 25 (89.3%), respectively. No patient in group A underwent exenteration. Eleven (78.6%) patients in group B underwent orbital exenteration. Of the 6 expired patients, 5 (83.3%) were in group B (P<0.0001). Peri-orbital ecchymosis and intracranial air extension were observed in 2 (13.3%) and 1 (6.7%) in group A patients, respectively.
Conclusions : Intra-orbital amphotericin injection under CT-guidance can be considered as a highly effective method in patients with orbital mucormycosis. This method may decrease exenteration without increasing mortality of patients.






comment