Comparison of fetal lung maturation in fetuses with intrauterine growth restriction with control group, using lung volume, lung/liver and lung/muscle signal intensity and apparent diffusion coefficient ratios on different magnetic resonance imaging sequences
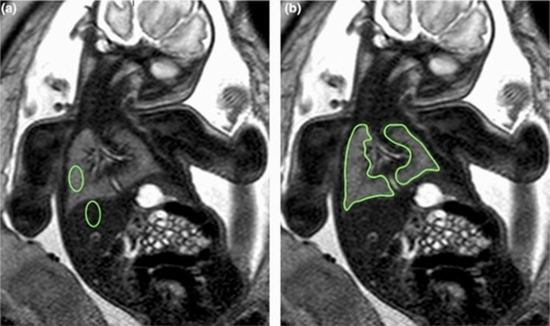
Purpose: To compare lung volume, lung apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and signal intensity ratio (SIR) on different magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences between intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) fetuses and the control group.
Materials and methods: 49 IUGR and 58 non-IUGR fetuses were imaged using 3 Tesla MRI units. Total lung volume (TLV), lung/liver SIR (LLSIR) and lung/muscle SIR (LMSIR) in T1 and T2-weighted sequences and lung/liver ADC ratio (LLADCR) and lung/muscle ADC ratio (LMADCR) were assessed.
Results: LLSIR and LMSIR were significantly higher in the T1-weighted sequence (p-value: .03) and LLADCR and LMADCR were significantly lower on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in IUGR fetuses compared to the control group (p-value: .01). There was no significant difference in SIRs in the T2-weighted sequence between the two groups. Although TLV was increased with gestational age in both groups, it was significantly lower in the IUGR group (mean: 82 ± 22.7 ml vs. 110.8 ± 18 ml, p-value: <.001).
Conclusion: The T1-weighted sequence and DWI seem to be better than the T2-weighted sequence for assessing the faint difference of lung maturity between groups. However, SIR differences were not as meaningful as TLV differences and this could be related to the complex maturation process in IUGR fetuses as the effect of higher endogenous corticosteroids





Send to friends