COVID-19 Evaluation by Low-Dose High Resolution CT Scans Protocol.
The December 2019 pneumonia of unknown origin outbreak in Wuhan, China, rapidly spread to all edge of the world; The responsible pathogen identified as the novel corona virus (2019), and the related pulmonary syndrome was named corona virus disease 2019 ( COVID-19) by the World Health Organization (1,2). Typical presenting clinical manifestations are cough and fever in addition to other nonspecific symptoms including, dyspnea, fatigue, headache, and muscle soreness (3). To date, (April 8th, 2020), confirmed cases passed 1.2 million people globally (4). Without any specific vaccines and/or treatment available, it is important to isolate infected patients. Social distancing is the most crucial strategy to save lives.
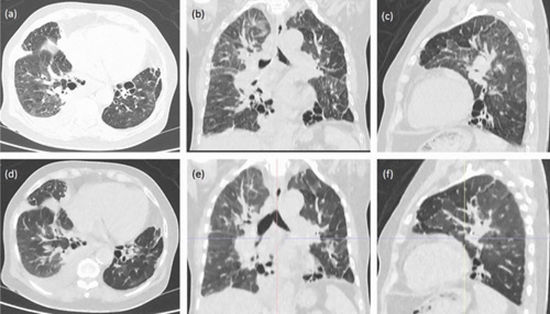
The diagnosis of COVID19 infection consists of detection of the viral RNA through swab samples via reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which is a time-consuming method with sub-optimal sensitivity (5), or detection of interstitial pneumonia by chest CT which is the hallmark of COVID-19 infection, even in asymptomatic patients (6). With the increasing number of people suspected of being infected, an inadequate number of RT-PCR kits is inevitable. Several studies have demonstrated the higher sensitivity of CT than RT-PCR in detecting COVID-19 infected patients (7). The high incidence of infected individuals in countries such as Iran, and the importance of pulmonary changes through the course of the disease demonstrate that chest CT is superior to RT-PCR (6). Due to the increasing number of chest CT scan requests by physicians and the need to reduce the risks of ionizing radiation a dose reduction protocol is needed which can be used with devices from different manufacturers.
We have designed a low-dose High Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) protocol for the Iranian Society of Radiology to evaluate individuals with a high probability of COVID-19 infection. Our protocol was developed to work with all CT scanners with 4 or more detectors and is defined for each manufacturer and model. Our primary goal of screening and evaluation is to detect COVID-19 infection in patients with highly suspicious clinical conditions and laboratory findings according to the ministry of health protocol. Therefore, the primary task is to detect ground glass opacities in the typical subpleural location. To reduce thoracic motion, the CT scan is to be performed in one breath-hold. The slice thickness of slices is 1-3 mm. Coronal and sagittal reconstructions would be optional. Maximum intensity projections as used for lung nodules is not mandatory. Neither oral nor intravenous contrast is used. The patient is supine, in the center of the gantry, with arms above the head. Images are obtained through the entire thorax. All patients are instructed to hold his and/or her breath at the end of inspiration during the entire scan. Suggested parameters to minimize the radiation dose are as follow: Kvp: 100-120, mAs: 50-100, Pitch: 0.8-1.5, Thickness: 1-3 mm. To conclude, low dose HRCT might have more advantages than RT-PCR especially in highly infected society with low availability of PCR-kits.






Send to friends