A case of fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma: a comparison between ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging findings
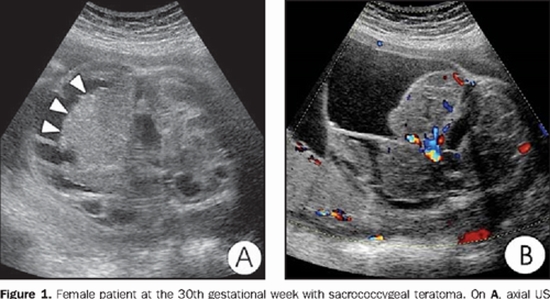
Sacrococcygeal teratomas are rare germ cell tumours associated with high perinatal and postnatal mortality and morbidity. We present a case of large fast growing (86x63mm) mostly cystic sacrococcygeal teratoma in a 27-year-old woman at 23 weeks of gestation with normal first trimester ultrasound exam. The mass has extended in to the fetal pelvis and displaced bladder anteriorly suggestive for type 2 sacrococcygeal teratoma. The fetus was evaluated by both Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and ultrasonography. Findings regarding tumour location, size and content were similar for both sonography and MRI, although vascular pattern was detected with higher accuracy and more details by colour Doppler sonography. On the other hand, MRI provide more appropriate information about tumour effects on surrounding tissue and conus location. Because of its mostly cystic components the margin of the intra-pelvic part was clearly visible by sonography but its boundary with adjacent buttock tissue was more vivid in MRI (a bit more clear in FIESTA compared to SS-FSE sequences). The parents chose termination of pregnancy especially based on the mass rapid growth. Based on parent's request karyotype evaluation and gene study was done on fetus, which revealed normal male fetus.






Send to friends