A heterozygous STXBP1 gene de novo mutation in an Iranian child with epileptic encephalopathy: Case report
The Syntaxin Binding Protein 1 (STXBP1) plays an important role in regulating neurotransmitter
release and synaptic vesicle fusion through binding to syntaxin-1A (STX1A) and changing its conformation.
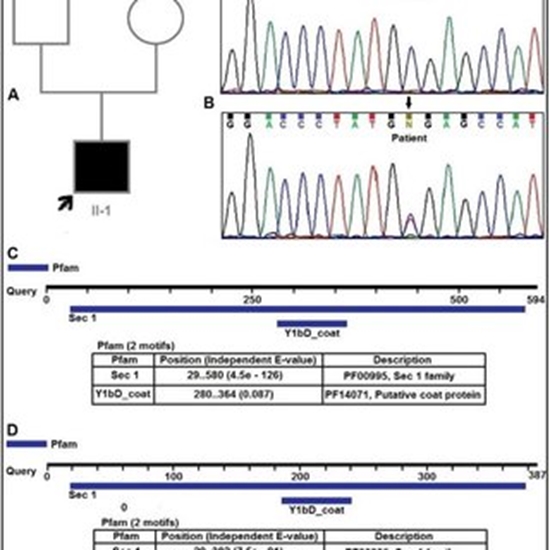
In this study, we identified a de novo mutation (c.C1162T: p.R388X) in exon 14 of the STXBP1 gene causing
an epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, non-epileptic movement, and unclassified infantile spasms
disorders in a 5-year-old boy by whole-exome sequencing. The segregation of this genetic variant was
examined in the patient as well as in his parents. We found the R388X in heterozygous state in the proband
but not in his parents. This genetic change could be due to de nova mutation or germlinemosaicism.
© 2019 Tehran University of Medical Sciences. All rights reserved






Send to friends