Agreement of Ultrasound Measures with POP-Q in Patients with Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Background:
Ultrasound has emerged as a valuable complimentary tool for assessment of pelvic organ prolapse (POP).Objectives:
The present study aimed to evaluate the correlation between ultrasound measures and clinical staging in patients with suspected POP.Patients and Methods:
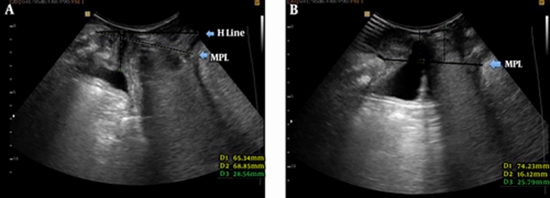
Forty women with clinical suspicion of POP were enrolled in this cross-sectional study between November 2011 and April 2012. Pelvic organ prolapse quantification (POP-Q) system was used for clinical staging. Perineal ultrasound was performed both at rest and during Valsalva maneuver after proper preparation. On mid sagittal view, two reference lines were drawn; midpelvic line (MPL) was defined as the inferior horizontal tangent of symphysis pubis and H line was drawn from the most inferior part of symphysis pubis to the anorectal junction. Spearman’s correlation coefficient and Kappa coefficient of agreements were used for statistical analysis.Results:
Forty women with the mean age of 49.9 ± 10.07 years were enrolled. Excellent correlation was seen between MPL and H line (rho = 0.91, 0.93 and 0.88 in anterior, apical and posterior compartments, respectively). POP-Q had good-to-excellent correlation with ultrasound (rho = 0.84, 0.78 and 0.63 for H line and rho = 0.89, 0.82, 0.71 for MPL in anterior, apical and posterior compartments respectively). In anterior and apical compartments, high agreement was seen between clinical and ultrasound staging methods when grouping patients to no prolapse/mild vs. moderate/severe. In the posterior compartment, this agreement was significant when grouping was done based on the presence or absence of POP.Conclusion:
Ultrasound has high correlation with POP-Q staging in all compartments for staging of pelvic organ prolapse. Ultrasound might be useful in the diagnosis of pop in those with negative clinical examination






Send to friends