Association of Different MRI BIRADS Descriptors With Malignancy in Non Mass-Like Breast Lesions
In this study we aimed to analyze the diagnostic role of MRI BIRADS features for diagnosis of malignancy in non mass like breast lesions.
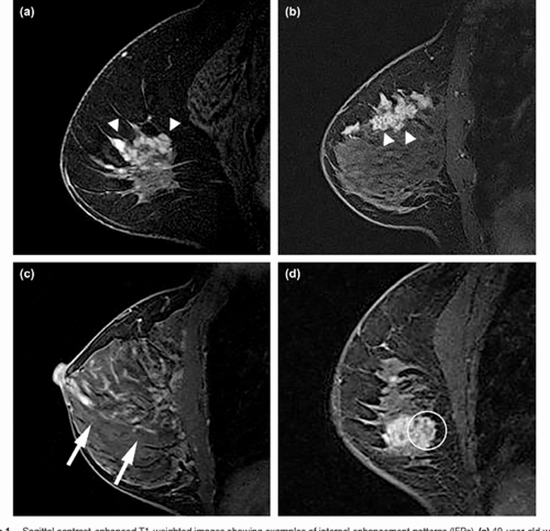
Background: Several studies on the diagnostic efficacy of MRI has not real consensus for the accuracy of MRI characteristics in non mass like breast lesions, and the number of malignant lesions in different studies is insufficient.
Objectives: In this study we aimed to analyze the diagnostic role of MRI BIRADS features for diagnosis of malignancy in non mass like breast lesions.
Patients and methods: All patients with positive findings (BIRADS 3, 4, 5), which had either biopsy proved pathology or follow-up MRI data at least for 12 months were included in the study. Finally, 213 breasts MRI that showed non mass like enhancing lesions among our patients were assessed in study. One experienced breast radiologist who was unaware of any clinical information or the histopathologic diagnosis evaluated all images retrospectively. The morphologic parameters evaluated consisted of distribution modifiers and pattern of internal enhancement. The kinetic enhancement parameters were assessed as showing washout, plateau, or persistent patterns. In the enhancement kinetic analysis, thew most worrisome curve type in each lesion was considered for interpretation, if it was more than 2% enhancement. We have evaluated the visual findings by comparison of the signal intensity on the first and third dynamic series. Data for the study were extracted from the breast MRI database and analyzed using SPSS version 16 statistical software.
Results: Totally 188 patients had 213 non mass like lesions. Mean age of the patients was 44.9 ± 8.3 years (24-63). Totally 46 of lesions were malignant (21.6%). The most common BIRADS score was 4 (116; 54.5%). The most prevalent feature of distribution, internal enhancement and curve type were focal (59.2%), clumped (27.2%) and washout (34.3%). Distribution of different subgroups of MR BIRADS features was different among benign and malignant lesions (All Pvalues < 0.05). Regarding association with malignancy, odds ratio of lesions with segmental or ductal linear distribution was 3.4 (95% CI = 1.7-6.8), Clumped, Reticular and Dendritic internal enhancement was 2.5 (95% CI = 1.3-5) and wash out curve type was 5.4 (95% CI = 2.7-10.9). Sensitivity of higher MR BIRADS (4,5) for diagnosis of malignancy was 100%. Specificity of segmental or ductal linear distribution in diagnosis of malignancy was 81%. Specificity of BIRADS 5 for diagnosis of malignancy was 98%. In a multivariate logistic regression analysis for diagnosis of malignancy in which distribution, internal enhancement and curve type were considered as independent variables, distribution and curve type remained significant in the model while the internal enhancement showed a borderline P-value.
Conclusions: Although in our study washout pattern was the most powerful indicator for malignant pathology in non mass like enhancing lesions, more studies with larger sample size needs in this regard.
Different MRI BIRADS Descriptors in Non Mass-Like Breast Lesions






Send to friends