Characterization of Active and Infiltrative Tumorous Subregions From Normal Tissue in Brain Gliomas Using Multiparametric MRI
Background: Targeted localized biopsies and treatments for diffuse gliomas rely on accurate identification of tissue subregions, for which current MRI techniques lack specificity
Purpose: To explore the complementary and competitive roles of a variety of conventional and quantitative MRI methods for distinguishing subregions of brain gliomas
Study type: Prospective
Population: Fifty-one tissue specimens were collected using image-guided localized biopsy surgery from 10 patients with newly diagnosed gliomas
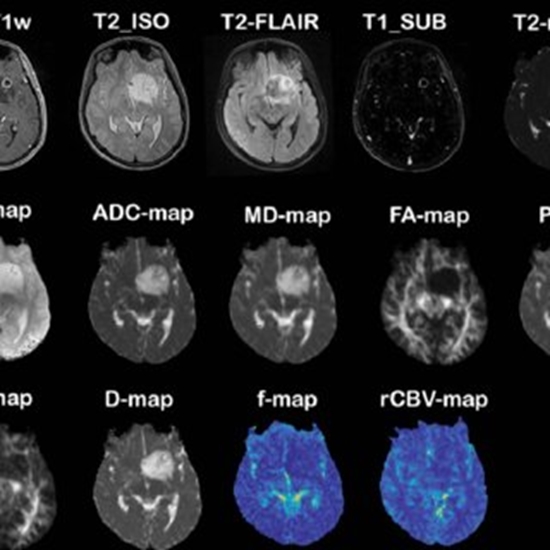
Field strength/sequence: Conventional and quantitative MR images consisting of pre- and postcontrast T1 w, T2 w, T2 -FLAIR, T2 -relaxometry, DWI, DTI, IVIM, and DSC-MRI were acquired preoperatively at 3T
Assessment: Biopsy specimens were histopathologically attributed to glioma tissue subregion categories of active tumor (AT), infiltrative edema (IE), and normal tissue (NT) subregions. For each tissue sample, a feature vector comprising 15 MRI-based parameters was derived from preoperative images and assessed by a machine learning algorithm to determine the best multiparametric feature combination for characterizing the tissue subregions.
Statistical tests: For discrimination of AT, IE, and NT subregions, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test and for pairwise tissue subregion differentiation, Tukey honest significant difference, and Games-Howell tests were applied (P < 0.05). Cross-validated feature selection and classification methods were implemented for identification of accurate multiparametric MRI parameter combination.
Results: After exclusion of 17 tissue specimens, 34 samples (AT = 6, IE = 20, and NT = 8) were considered for analysis. Highest accuracies and statistically significant differences for discrimination of IE from NT and AT from NT were observed for diffusion-based parameters (AUCs >90%), and the perfusion-derived parameter as the most accurate feature in distinguishing IE from AT. A combination of "CBV, MD, T2 _ISO, FLAIR" parameters showed high diagnostic performance for identification of the three subregions (AUC ∼90%).
Data conclusion: Integration of a few quantitative along with conventional MRI parameters may provide a potential multiparametric imaging biomarker for predicting the histopathologically proven glioma tissue subregions






Send to friends