Chest CT scan features to predict COVID 19 patients’ outcome and survival
Background
Providing efficient care for infectious coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients requires an accurate and accessible tool to medically optimize medical resource allocation to high-risk patients.
Purpose
To assess the predictive value of on-admission chest CT characteristics to estimate COVID-19 patients' outcome and survival time.
Materials and Methods
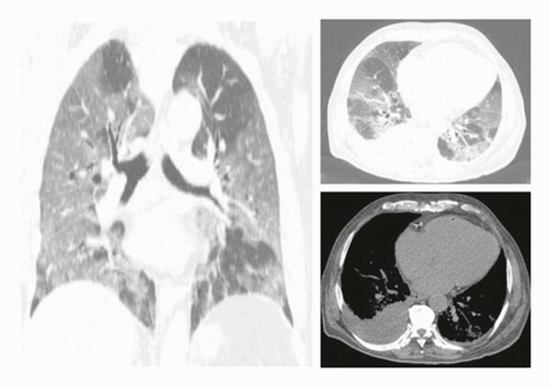
Using a case-control design, we included all laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patients who were deceased, from June to September 2020, in a tertiary-referral-collegiate hospital and had on-admission chest CT as the case group. The patients who did not die and were equivalent in terms of demographics and other clinical features to cases were considered as the control (survivors) group. The equivalency evaluation was performed by a fellowship-trained radiologist and an expert radiologist. Pulmonary involvement (PI) was scored (0–25) using a semiquantitative scoring tool. The PI density index was calculated by dividing the total PI score by the number of involved lung lobes. All imaging parameters were compared between case and control group members. Survival time was recorded for the case group. All demographic, clinical, and imaging variables were included in the survival analyses.
Results
After evaluating 384 cases, a total of 186 patients (93 in each group) were admitted to the studied setting, consisting of 126 (67.7%) male patients with a mean age of 60.4 ± 13.6 years. The PI score and PI density index in the case vs. the control group were on average 8.9 ± 4.5 vs. 10.7 ± 4.4 (p value: 0.001) and 2.0 ± 0.7 vs. 2.6 ± 0.8 (p value: 0.01), respectively. Axial distribution (p value: 0.01), cardiomegaly (p value: 0.005), pleural effusion (p value: 0.001), and pericardial effusion (p value: 0.04) were mostly observed in deceased patients. Our survival analyses demonstrated that PI score ≥ 10 (p value: 0.02) and PI density index ≥ 2.2 (p value: 0.03) were significantly associated with a lower survival rate.
Conclusion
On-admission chest CT features, particularly PI score and PI density index, are potential great tools to predict the patient's clinical outcome






comment