Coronary CT Angiography and Dual-Energy Computed Tomography in Ischemic Heart Disease Suspected Patients
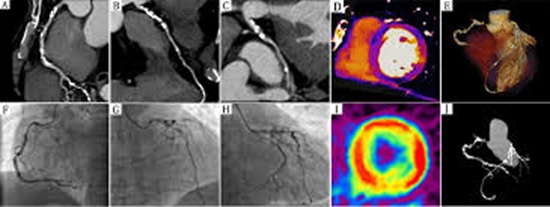
Background: Advanced computed tomography (CT) scanners enable concurrent assessment of coronary artery anatomy and myocardial perfusion. The purpose of this study was to assess dual-energy CT images in a group of patients suspected for ischemic heart disease and to evaluate agreement of cardiac computed tomography perfusion (CTP) images with CT angiography results in a single dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) acquisition.
Methods: Thirty patients (mean age: 53.8 ± 12.9 years, 60% male) with angina pectoris or atypical chest pain, suspected for ischemic heart disease, were investigated using a 384-row detector CT scanner in dual-energy mode (DECT). Firstly, resting CTP images were acquired, and then from the same raw data, computed tomography angiography (CTA) studies were reconstructed for stenosis detection. CT-based dipyridamole-stress myocardial perfusion imaging was then performed in patients who exhibited coronary stenosis >50% or had myocardial bridge (MB). A color-coded iodine map was used for evaluation of myocardial perfusion defects using the 17-segment model. Two independent blinded readers analyzed all images for stenosis and myocardial perfusion defects. Different myocardial iodine content (mg/mL) was calculated by parametric tests. The kappa agreement was calculated between results of two methods in cardiac scans.
Results: All 30 CT angiograms were evaluated and assessment ability was 100% for combined CTA/CTP. According to the combined CT examination, 17 patients (56.7%) exhibited significant coronary stenosis and/or deep MB (DMB). A total of 510 myocardial segments and 90 vascular territories were analyzed. Coronary CTA demonstrated significant stenosis in 22 vessels (24.4% of all main coronary arteries) among 12 patients (40%), DMB in 6 vessels (6.7% of all main coronary arteries) in 17 out of 30 patients (56.7%). Twenty-eight out of 90 vascular territories (31.1%) and 41 out of 510 segments (8%) showed reversible perfusion defects on stress DECT. Kappa agreement between CTA and CTP results in whole heart was 0.79 (95% confidence interval=0.57-1). There were significant differences in mean iodine concentration between ischemic (0.59 ± 0.07 mg/mL) and normal segments (2.2 ± 0.15) with P < 0.001.
Conclusion: Agreement of CTA and CTP in whole heart and in LAD considering DMB and significant CAD together were good to excellent; however, considering sole pathologies, most of the agreements were weak (<0.5). DECT with iodine quantification may provide a valuable method in comparison with previous methods for identifying both coronary stenosis and myocardial ischemia






Send to friends