Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient values and peritumoral edema with pathologic biomarkers in patients with breast cancer
Purpose: To investigate the relationship between breast cancer imaging features on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and histopathological characteristics.
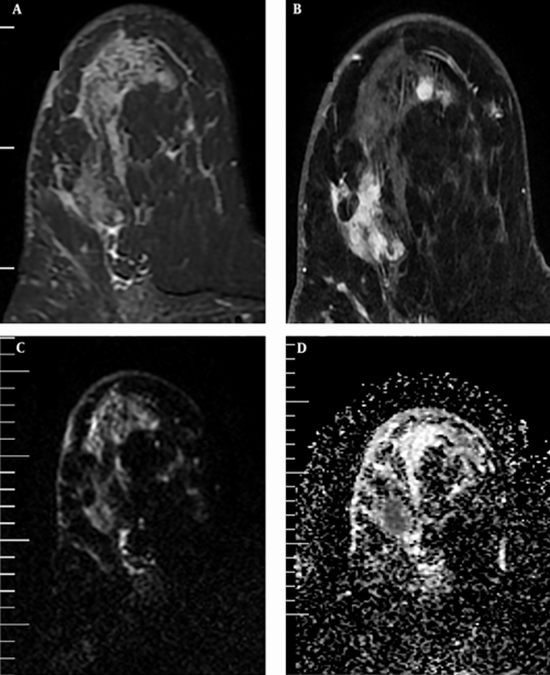
Methods and materials: We prospectively enrolled 46 patients who underwent 1.5-T MRI with 68 breast malignant lesions from 2017 until 2019. Peritumoral edema was determined based on visual assessment on T2 weighted imaging. Lesions were categorized into two groups: A: with edema (48 lesions) and B: without edema (20 lesions).
Results: The tumor size was not different among two groups but multifocal-multicentric lesions were more common in the group A (70% vs. 35%). The axillary lymph nodes are most involved in group A. ER and PR positive lesions were more common in group B (90% vs. 56.3%) but in the group A, HER2 positive lesions were found to be more common (31.3% vs. 15%). The mean ADC value in tumors and peritumoral regions were lower (0.97 × 10-3 mm2/s, P = 0.023) and higher (1.85 × 10-3 mm2/s, P < 0.0001) in group A, respectively. Peritumoral ADC value was significantly higher in HER2-positive group.
Conclusion: Breast carcinomas with peritumoral edema were found to be more multifocal-multicentric, with higher prevalence of axillary lymph node involvement, more HER 2-positive, with lower prevalence of ER/PR-positive, lower tumoral ADC and higher peritumoral ADC values






Send to friends