Design and Validation of Synchronous QCT Calibration Phantom: Practical Methodology
Introduction: Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) can supplement dual x-ray absorptiometry by enabling geometric and compartmental bone assessments. Whole-body spiral CT scanners are widely available and require a short scanning time of seconds, in contrast to peripheral QCT scanners, which require several minutes of scanning time. This study designed and evaluated the accuracy and precision of a homemade QCT calibration phantom using a whole-body spiral CT scanner.
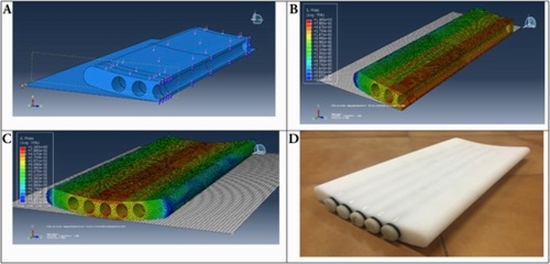
Materials and methods: The QCT calibration phantom consisted of K2HPO4 solutions as reference. The reference material with various concentrations of 0, 50, 100, 200, 400, 1000, and 1200 mg/cc of K2HPO4 in water were used. For designing the phantom, we used the ABAQUS software.
Results: The phantoms were used for performance assessment of QCT method through measurement of accuracy and precision errors, which were generally less than 5.1% for different concentrations. The correlation between CT numbers and concentration were close to one (R2 = 0.99).
Discussion: Because whole-body spiral CT scanners allow central bone densitometry, evaluating the accuracy and precision for the easy to use calibration phantom may improve the QCT bone densitometry test.
Conclusion: This study provides practical directions for applying a homemade calibration phantom for bone mineral density quantification in QCT technique.






Send to friends