Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasound in Determining the Cause of Bilious Vomiting in Neonates
This study suggested that in cases in which US makes a certain diagnosis, its accuracy eliminates the need for further diagnostic tests, but if it is inconclusive, further radiological contrast studies should be tried to make the final diagnosis.
Background
Plain radiography and contrast radiologic studies are traditionally the main options in evaluating neonates presenting with bilious vomiting. While ultrasonography (US) is more available, its diagnostic accuracy is in question.
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to determine the diagnostic accuracy of US in evaluating these patients with bilious vomiting.
Patients and Methods
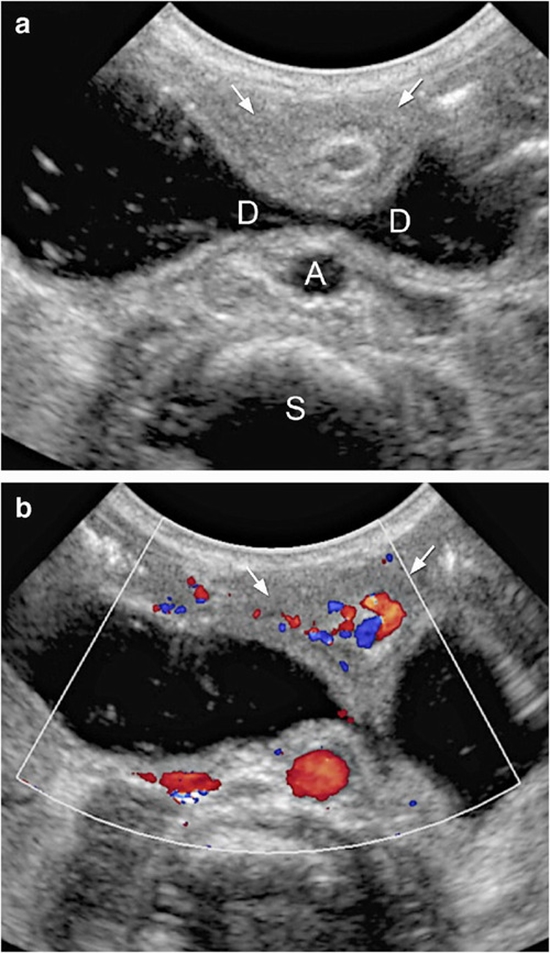
All neonates with bilious vomiting or bilious nasogastric tube drainage presented to a children’s hospital in a 1.5-year period were included. US were performed in all patients. The results were compared with clinical and radiological data and the final diagnosis. We used chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests for analysis.
Results
The cause of bilious vomiting for 18 of the 23 included patients was surgical. All patients labeled as surgical candidates by US ended in surgery [positive predictive value (PPV) = 100%], while only 50% of the patients with inconclusive US were operated [negative predictive value (NPV) = 50%, Confidence Interval (CI) 95%: 29%-71%]. The sensitivity and specificity of US in diagnosing intestinal atresia (n = 9) was 89% [CI 95%: (68% - 100%)] and 100%. In cases with malrotation (n = 4) and midgut volvulus (n = 2), sonographic diagnosis was in concordance with final surgical diagnosis.
Conclusion
This study suggested that in cases in which US makes a certain diagnosis, its accuracy eliminates the need for further diagnostic tests, but if it is inconclusive, further radiological contrast studies should be tried to make the final diagnosis.






Send to friends