Diagnostic accuracy of radiologic scoring system for evaluation of suspicious hirschsprung disease in children
Our objective was to devise another scoring system that uses a checklist of radiologic and clinical signs to determine the probability of HD in suspicious patients
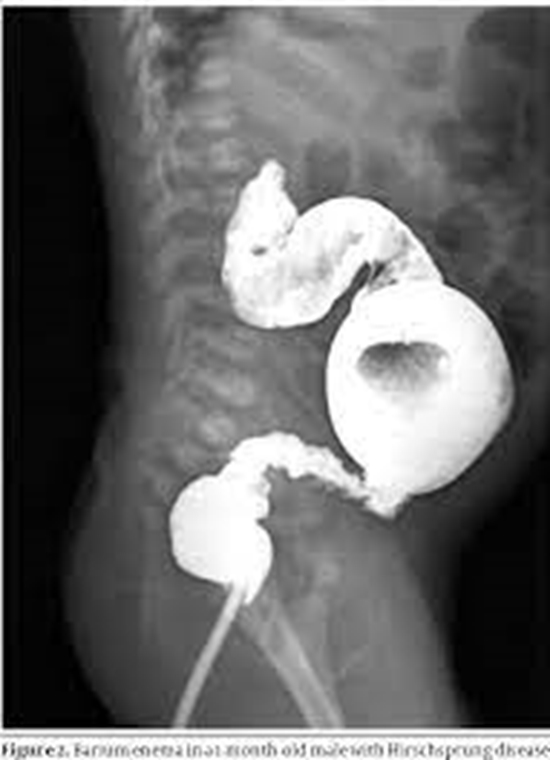
Objectives:
Our objective was to devise another scoring system that uses a checklist of radiologic and clinical signs to determine the probability of HD in suspicious patients.
Patients and Methods:
In a diagnostic accuracy study, 55 children with clinical manifestations of HD that referred to a training hospital from 1998 to 2011 were assessed. A checklist was used to evaluate the items proposed by contrast enema (CE), based on six subscales, including transitional zone, rectosigmoid index (RSI), irregular contractions in aganglionic region, cobblestone appearance, filling defect due to fecaloid materials and lack of meconium defecation during the first 48 hours after birth. The patients were classified as high score and low score. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of our scoring system were calculated for identifying HD, in comparison with pathologically proved or ruled out HD.
Results:
Of the 55 patients, 36 (65.4%) cases had HD and 19 (34.6%) cases were without HD. In the HD group, 32 patients showed high scores and four patients had low scores. The sensitivity and specificity of our diagnostic scoring system were 88.9% (95% CI: 78.6% - 99.1%) and 84.2% (95% CI: 68.7% - 100%), respectively. Moreover, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were 91.4% (95% CI: 82.1% - 100%) and 80% (95% CI: 62.5% - 97.5%), respectively.
Conclusions:
Our new scoring system of CE is a useful diagnostic method in HD. If a patient’s score is high, that patient is highly suspicious to HD and reversely, when one’s score is low, the patient presents a reduced probability to be diagnosed with HD.






Send to friends