Diagnostic models for detection of intrauterine growth restriction and placental insufficiency severity, based on magnetic resonance imaging of placenta
Purpose: We aimed to provide diagnostic models based on different parameters of placental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), as well as the severity of placental insufficiency.
Material and methods: We included 44 foetuses with appropriate weight for gestational age (AGA) and 46 foetuses with documented IUGR, defined as the estimated foetal weight (EFW) below the 10th centile. Using Doppler ultrasound, IUGR cases were divided into 2 groups: 1) IUGR with severity signs: EFW < 3rd centile, or cerebroplacental ratio < 5th centile, or abnormal umbilical/uterine artery pulsatility index; and 2) non-severe IUGR without any of this criterion. For all these participants, placental MRI was performed in the third gestational trimester, and its parameters were compared between AGA and IUGR, as well as between the severe and non-severe IUGR groups. Two diagnostic models consisting of significant predictors were developed, and their performance was investigated with accuracy metrics.
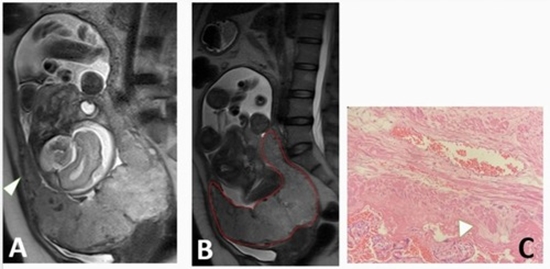
Results: The severity signs were detected in 25 (54.3%) IUGR cases. The diagnostic model for the differentiation of IUGR from AGA revealed an acceptable performance (area under the curve [AUC] of 0.749) and consisted of 2 variables: 1) the largest size of infarct ≥ 25 mm (odds ratio [OR] = 5.01, p = 0.001), and 2) thickness : volume ratio ≥ 0.043 (OR = 3.76, p = 0.027); while, the logistic regression model for detection of the severity signs was even better, with AUC = 0.862, and comprised of 2 predictors: 1) placental infarct percent ≥ 10% (OR = 26.73, p = 0.004), and 2) placental globular shape (OR = 5.40, p = 0.034).
Conclusions: Placental MRI parameters can differentiate IUGR from AGA, and more precisely, assess the severity of placental insufficiency in IUGR foetuses.






Send to friends