Diagnostic value of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging in discriminating between metastatic and non metastatic pelvic lymph nodes in endometrial cancer
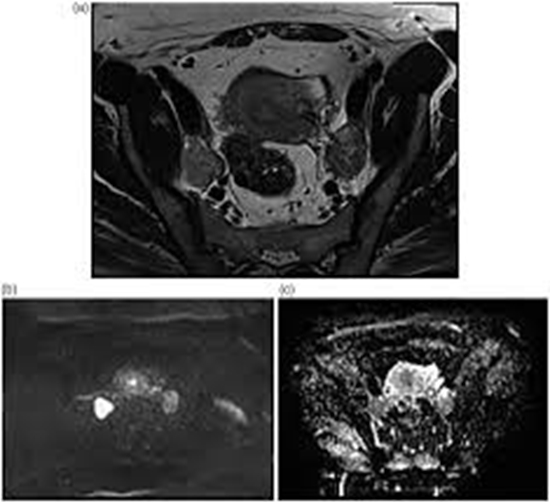
Background: Researchers have recently focused on assessing the accuracy of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in predicting pelvic lymph node metastases in gynecological malignancies.
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic value of DW-MRI in discriminating between metastatic and non-metastatic pelvic lymph nodes in endometrial cancer patients.
Material and methods: This retrospective database study was conducted with 33 women aged 30-84 years with pathologically proven endometrial cancer that had been assessed by DW-MRI before their first treatment initiation at our referral hospital from March 2016 to April 2019. The diffusion technique (b = 50, 400, and 1000 mm2/s) was used in the imaging, and continuous apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) metrics (ADCmin, ADCmax, ADCmean, ADCSD, and rADC) were compared between the metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes.
Results: In total, 48 lymph nodes from 33 patients were assessed. All metastatic lymph nodes were restricted, while among the non-metastatic lymph nodes, only 19.3% were restricted. Considering pathological reports of metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes as the gold standard, DWI-related restricted and non-restricted features had a sensitivity of 80.6%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 87.5% to discriminate between a metastatic and non-metastatic pattern. ADC metrics of ADCmin, ADCmax, ADCmean, ADCSD, and rADC showed high values enabling differentiation between metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes. The best cut-off values were 0.7 × 10-3, 1.2 × 10-3, 1.01 × 10-3, 123, and 0.78, respectively.
Conclusion: DW-MRI is a useful quantitative tool for differentiating between metastatic and benign lymph nodes in endometrial cancer patients.
Keywords: Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; endometrial neoplasm; lymph nodes; lymphatic metastasis.






Send to friends