Identification of Two Novel Mutations in PKHD1 Gene from Two Families with Polycystic Kidney Disease by Whole Exome Sequencing
Background
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an autosomal recessive disorder resulting from mutations in the PKHD1 gene on chromosome 6 (6p12), a large gene spanning 470 kb of genomic DNA.
Objective
The aim of the present study was to report newly identified mutations in the PKHD1 gene in two Iranian families with PKD.
Materials and Methods
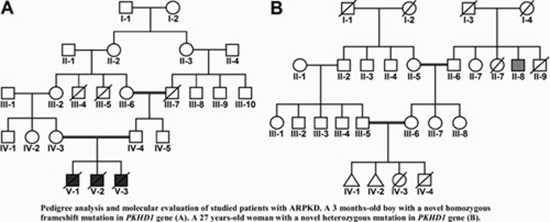
Genetic alterations of a 3-month-old boy and a 27-year-old girl with PKD were evaluated using whole-exome sequencing. The PCR direct sequencing was performed to analyse the co-segregation of the variants with the disease in the family. Finally, the molecular function of the identified novel mutations was evaluated by in silico study.
Results
In the 3 month-old boy, a novel homozygous frameshift mutation was detected in the PKHD1 gene, which can cause PKD. Moreover, we identified three novel heterozygous missense mutations in ATIC, VPS13B, and TP53RK genes. In the 27-year-old woman, with two recurrent abortions history and two infant mortalities at early weeks due to metabolic and/or renal disease, we detected a novel missense mutation on PKHD1 gene and a novel mutation in ETFDH gene.
Conclusion
In general, we have identified two novel mutations in the PKHD1 gene. These molecular findings can help accurately correlate genotype and phenotype in families with such disease in order to reduce patient births through preoperative genetic diagnosis or better management of disorders.






Send to friends