Multi-organ infarction following percutaneous transhepatic esophageal variceal obliteration with glue injection: a case report
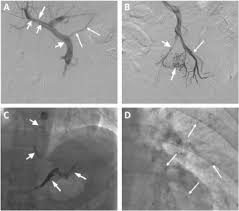
Percutaneous transhepatic variceal obliteration (PTVO) is currently one of the best treatment options for controlling acute recurrent bleeding in cirrhotic patients. Nevertheless, this procedure is associated with major and minor complications such as fever, pain, fatal intraperitoneal hemorrhage, and rarely, embolization of embolic agents to the systemic circulation. Only one study has reported systemic emboli following the use of glue-lipiodal mixture for percutaneous transhepatic embolization of esophageal varices and here we report another case of this complication. Here, we report a 44-year-old man presenting with multi-organ infarction following PTVO with glue-Lipiodol mixture. He was a known case of liver cirrhosis who was admitted for recurrent bleeding from esophageal varices. The patient became a candidate for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt surgery; however, he did not provide consent for this procedure. the patient eventually decided to undergo PTVO as an alternative option. Twelve hours after the procedure, the patient developed neurological symptoms such as left side weakness, dysarthria, and fecal incontinence. Further investigation showed glue particles in brain, liver, spleen and both lungs. Contrast echocardiography and splenoportography did not show any evidence of right-to-left shunt. Thus, conservative management was initiated for the patient, which resulted in the gradual improvement after three weeks. Prior evaluation with splenoportography and contrast echocardiography before performing PTVO may help in the early detection of any connection with systemic circulation. Also, based on the desired procedure, the most appropriate glue/Lipiodol ratio and injection technique should be selected to minimize the risk of adverse events






Send to friends