Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs): the predictive value of MDCT characteristics in the differentiation of histopathological grades
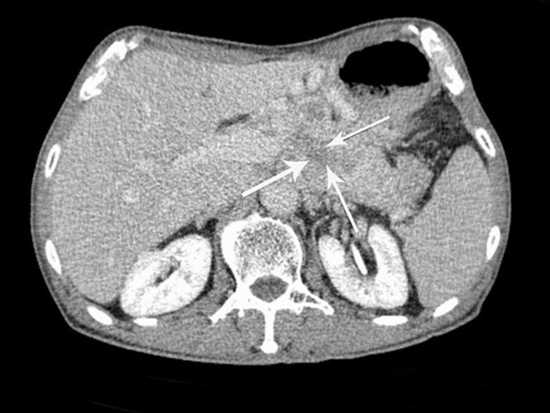
Purpose: To investigate the correlation between multiple detector computed tomography (MDCT) features of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs) and histopathologic grade and find valuable imaging criteria for grade prediction.
Material and methods: MDCT of 61 patients with 65 masses, which pNETs were approved histopathologically, underwent revision retrospectively. Each MDCT was evaluated for various radiologic characteristics. Absolute and relative (R: tumor/pancreas, D: tumor-pancreas) tumor enhancements were calculated in multiple post contrast phases.
Results: 61 patients [mean age = 50.70 ± 14.28 y/o and 30(49.2%) were male] were evaluated and classified into 2 groups histopathologically: G1: 32 (49.2%) and G2,3: 33 (50.8%). Significant relationships were observed between histopathologic tumor grade regarding age (p = 0.006), the longest tumor size (p = 0.006), presence of heterogeneity (p < 0.0001), hypodense foci in delayed phase (p = 0.004), lobulation (p = 0.002), vascular encasement (p < 0.0001), adjacent organ invasion (p = 0.01), presence (p < 0.0001) and number (0.02) of liver metastases, presence of lymphadenopathy with short axis of more than 10 mm (LAP) (p = 0.008), pathologic lymph node size (p = 0.004), relative (R and D) (p = 0.05 and 0.02, respectively), and percentage of arterial hyper-enhancing area (p = <0.0001). Tumor grades, however, had no significant relationship with gender, tumor location, tumor outline, calcification, cystic change, or pancreatic (PD) or biliary duct (BD) dilation (p = 0.21, 0.60, 0.05, 0.05 1, 0.10, and 0.51, respectively). Then, we suggested a novel imaging criteria consisting of six parameters (tumor size > 33 mm, relative (R) tumor enhancement in arterial phase ≤ 1.33, relative (D) tumor enhancement in arterial phase ≤ 16.5, percentage of arterial hyper-enhancing area ≤ 75%, vascular encasement, and lobulation), which specificity and accuracy of combination of all findings (6/6) for predicting G2,3 were 100% and 70.1%, respectively. The highest accuracy (84.21%) was seen in combinations of at least 4 of 6 findings, with 80.00% sensitivity, 87.5% specificity, 83.33% PPV, and 84.85% NPV.






Send to friends