Predicting factors for relapse in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis: results from a long term cohort
Objective: To investigate the predictive factors and the best predictive model for relapse in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) patients.
Methods: All patients referred to our tertiary university hospital with confirmed diagnosis of GPA based on 1990-ACR criteria and/or revised Chapel Hill nomenclature, who were followed more than 24 months between 2012 and 2021 were included. Patients were classified into relapsing and non-relapsing groups. Disease activity was assessed based on Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) and BVAS for GPA (BVAS-GPA). All demographic, clinical, laboratory, and radiologic parameters were compared between two groups.
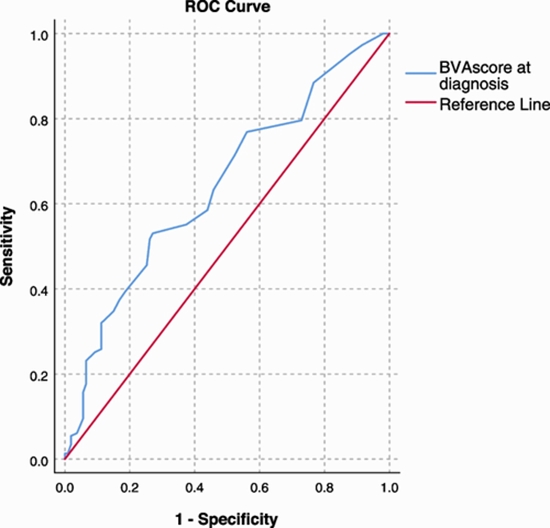
Results: Data of 133 patients (male = 52 (39.1%); mean age = 46.5 ± 14.5 years) with a mean follow-up period of 49.4 ± 24.1 months were evaluated. Of those, 91 (68.4%) experienced at least one relapse episode. The mean duration of relapse-free-survival (RFS) was 12.5 months with 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year RFS rates of 46.6%, 34.6%, and 31.6%, respectively. The risk of relapse was higher if patients had higher BVAS or BVAS-GPA score (P-values < 0.001), constitutional syndrome (P-value = 0.01), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (P-value = 0.01), C-reactive-protein (P-value = 0.03), alanine transaminase > 40 units/L (P-value = 0.04), and microscopic hematuria (P-value = 0.001). In backward logistic regression analysis, baseline BVAS score ≥ 12 (Ex(B) = 4.21, P-value = 0.03), and NLR > 2.5 (Ex(B) = 12.00, P-value = 0.007) remained statistically significant at the last step of the model with 75.8% sensitivity, 76.9% specificity, and 76.3% accuracy in predicting the relapsing patients. The frequency of relapse episodes was significantly lower in treatment group of rituximab-rituximab (0.3 ± 0.6) compared to cyclophosphamide-methotrexate (1.2 ± 1.3) and cyclophosphamide-azathioprine (1.8 ± 1.5) treatment protocols (P-value = 0.002).
Conclusion: High-risk patients according to proposed model should be prioritized for more intensive care, more aggressive treatment, and closer follow-ups






comment