Safety and efficacy study of allogeneic human menstrual blood stromal cells secretome to treat severe COVID 19 patients: clinical trial phase I & II
Background: Cell-free Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been considered due to their capacity to modulate the immune system and suppress cytokine storms caused by SARS-CoV-2. This prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of secretome derived from allogeneic menstrual blood stromal cells (MenSCs) as a treatment in patients with severe COVID-19.
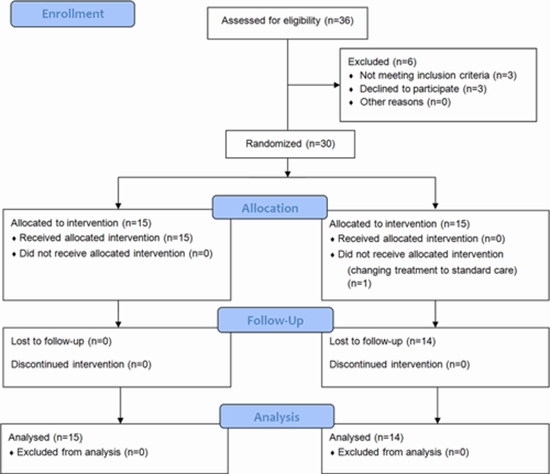
Methods: Patients with severe COVID-19 were randomized (1:1) to either MenSC-derived secretome treatment or the control group. Subjects received five intravenous infusions of 5 mL secretome or the same volume of placebo for five days and were monitored for safety and efficacy for 28 days after treatment. Adverse events, laboratory parameters, duration of hospitalization, clinical symptom improvement, dynamic of O2 saturation, lymphocyte number, and serial chest imaging were analyzed.
Results: All safety endpoints were observed without adverse events after 72 h of secretome injection. Within 28 days after enrollment, 7 patients (50%) were intubated in the treated group versus 12 patients (80%) in the control group. Overall, 64% of patients had improved oxygen levels within 5 days of starting treatment (P < 0.0001) and there was a survival rate of 57% in the treatment group compared to 28% in the control group was (P < 0.0001). Laboratory values revealed that significant acute phase reactants declined, with mean C-reactive protein, ferritin, and D-dimer reduction of 77% (P < 0.001), 43% (P < 0.001), and 42% (P < 0.05), respectively. Significant improvement in lymphopenia was associated with an increase in mean CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocyte counts of 20% (P = 0.06) and 15% (P < 0.05), respectively. Following treatment, percentage of pulmonary involvement showed a significant improvement in the secretome group (P < 0.0001). This improvement differed significantly between survivors and those who were dying (P < 0.005).
Conclusions: For the first time, this study demonstrated that in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19, therapy with MenSCs-derived secretome leads to reversal of hypoxia, immune reconstitution, and downregulation of cytokine storm, with no adverse effects attributable to the treatment. Given these outcomes, it may be possible to use this type of treatment for serious inflammatory lung disease with a mechanism similar to COVID-19 in the future. However, it is necessary to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MenSCs-derived secretome therapy in clinical trials on a larger population of patients.






comment