Segmentation of uterine using neighborhood information affected possibilistic fcm and gaussian mixture model in uterine fibroid patients MRI
In this paper, we proposed an automatic method for segmentation of uterus in MRIs
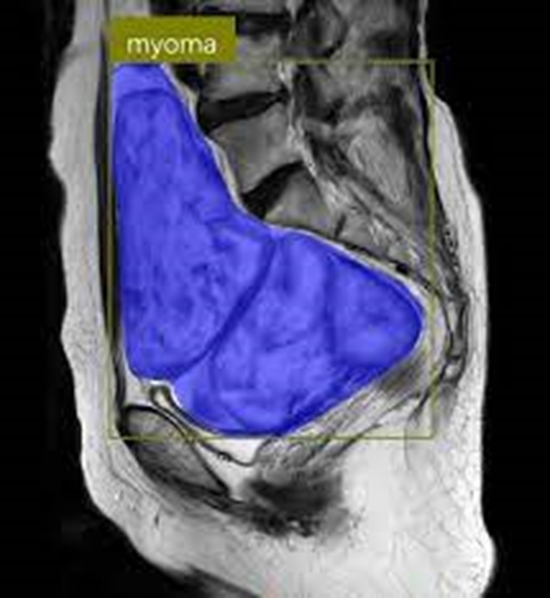
Uterine ¯broids are common tumors of female pelvis. Uterine volume measurement before and after surgery has an important role in predicting the outcome and later on in comparing with the result of the uterine ¯broid shrinkage surgery. Because of inhomogeneity and di®erent shapes and sizes of uterus and ¯broids, segmentation of uterus is a di±cult task. In this paper, using T1 and Enhanced-T1 MR images uterine is initially segmented using a new clustering algorithm named neighborhood information a®ected possibilistic fuzzy C-means (NIAPFCM). NIAPFCM uses membership, typicality and spatial neighborhood information to cluster each voxel. Finally, the redundant parts are removed by superimposing the segmented region of the T1-enhanced image over the registered T1 image. Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is applied to the extracted region histogram as a model for accurate tresholding. The results obtained using the proposed method are evaluated by comparing with manual segmentations using volume-based and distance-based metric methods. Also, the result of NIAPFCM is compared with fuzzy C-means (FCM) and possibilistic fuzzy C-means (PFCM) algorithms. We found this algorithm e±cient, which provides good and reliable results.






Send to friends