Test-retest reliability of nerve and muscle morphometric characteristics utilizing ultrasound imaging in individuals with unilateral sciatica and controls
Background: Ultrasound imaging has been suggested for studying the structure and function of nerves and muscles; however, reliability studies are limited to support the usage. The main aim of this study was to explore the intrarater within-session reliability of evaluating the sciatic nerve and some related muscles morphology by ultrasound imaging.
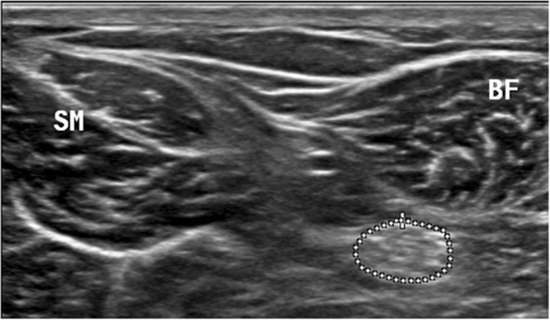
Methods: Three B-mode images from two scans (transverse and longitudinal) were acquired from the multifidus, biceps femoris, soleus and medial gastrocnemius muscles bilaterally from 15 participants with sciatica and 15 controls in one session, 1-h apart. The data were collected from March to July 2017. Contraction ratio was measured only by longitudinal scan, while the echo intensity was measured using maximum rectangular region of interest in two scans (transverse and longitudinal) for all muscles. Cross-sectional area, direct (tracing) and indirect (ellipsoid formula) methods were used to measure the sciatic nerve. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC 3,1), standard error of measurement and minimal detectable change were calculated. Results: Good to high ICCs (0.80–0.96) were found for muscle contraction ratio in the longitudinal scans in all the muscles in both sciatica and control groups. For echo intensity measurements ICCs ranged from moderate to high, with higher ICCs seen with the maximum region of interest in the transverse scans. The minimal detectable change values ranged between 0.11 and 0.53 cm for contraction ratio.
Conclusions: Ultrasound imaging has high intrarater within-session reliability for assessing the sciatic nerve Cross- sectional area and muscle contraction ratios. Transverse scans with the maximum region of interest result in higher reliability. The sciatic Cross-sectional area is most accurately measured utilizing the direct tracing method rather than the indirect ellipsoid method.






Send to friends