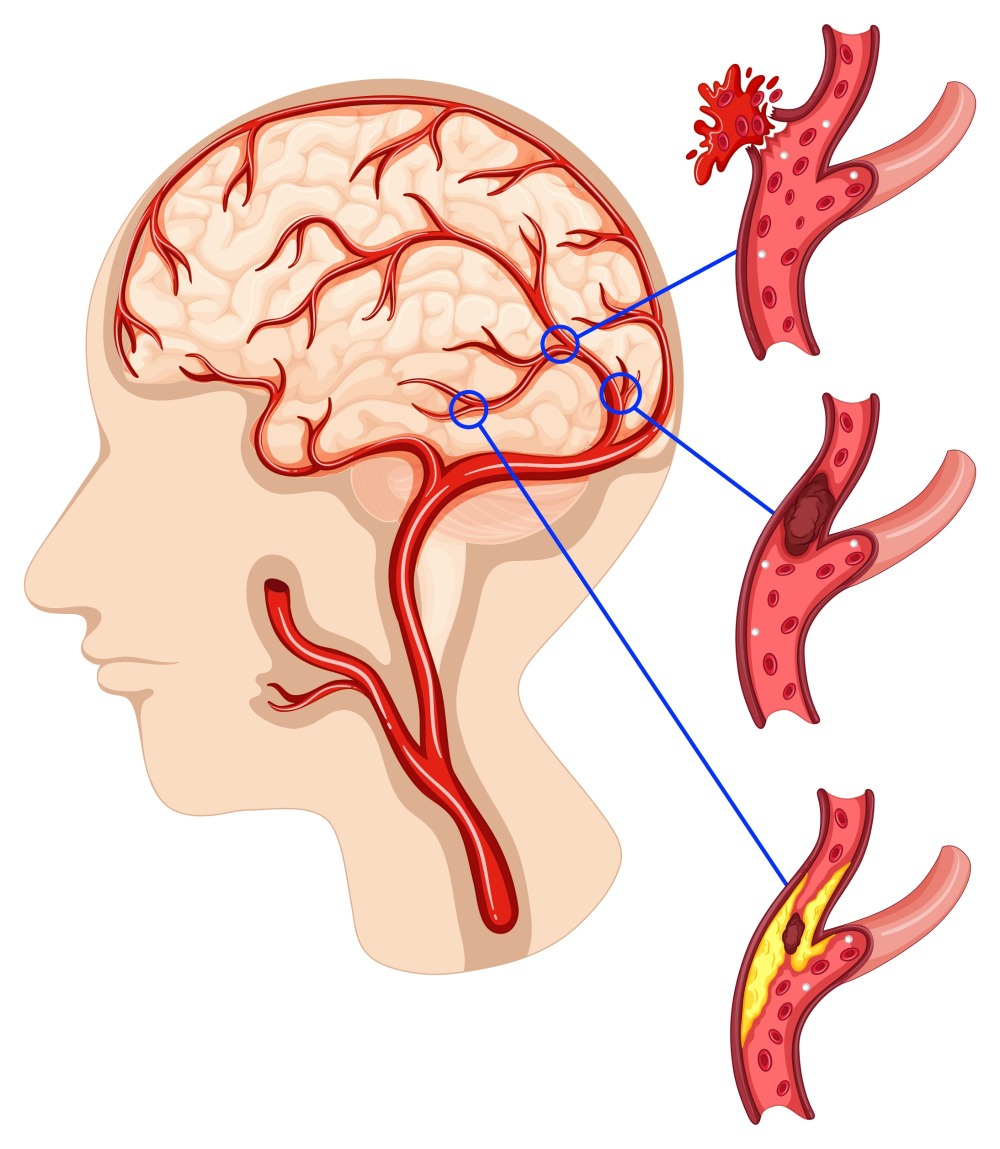
آنوریسم
A cerebral aneurysm is a localized dilation or bulging of a blood vessel in the brain, typically caused by a weakness in the vessel wall. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can lead to a life-threatening condition known as subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), often resulting in severe disability or death. Early diagnosis and proper management are critical for preventing these devastating outcomes.
Types of Cerebral Aneurysms

Aneurysms are classified based on shape and location, including:
-
Saccular Aneurysm (Berry Aneurysm): The most common type, characterized by a balloon-like sac protruding from the vessel wall.
-
Fusiform Aneurysm: A spindle-shaped dilation affecting the entire circumference of the vessel.
-
Pseudoaneurysm: A false aneurysm resulting from arterial wall injury, often due to trauma or infection.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
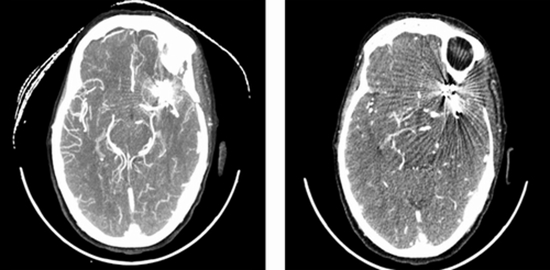
Many aneurysms are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally during imaging studies such as MRI, CT, or cerebral angiography. However, rupture presents with alarming symptoms such as:
-
Sudden and severe headache (thunderclap headache)
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Seizures
-
Neurological deficits (e.g., visual disturbances, paralysis)
Definitive diagnosis is typically achieved through Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA), which allows for detailed visualization of cerebral vessels and treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Treatment selection depends on factors such as aneurysm size, location, morphology, and patient health status. The two primary treatment approaches are:
1. Surgical Clipping:
Involves a craniotomy to expose the aneurysm and placing a metallic clip at its neck to block blood flow.
2. Endovascular Treatment:
A minimally invasive approach performed via the vascular system, with embolization (coiling) being the most prominent technique.
Endovascular Embolization (Coiling)
Definition:
Endovascular embolization involves threading a catheter through the femoral artery up to the cerebral vessels, then inserting small platinum coils into the aneurysm sac to promote clotting and isolate the aneurysm from blood circulation.
Advantages of Coiling:
Common Techniques:
-
Simple Coiling: Suitable for narrow-necked aneurysms.
-
Balloon-Assisted Coiling: Used for wide-neck aneurysms, employing a temporary balloon for stability.
-
Stent-Assisted Coiling: Uses a permanent stent to support coil placement.
-
Flow Diverters: Specialized stents that redirect blood flow away from the aneurysm to promote thrombosis within the sac.
Post-Treatment Care
Patients undergoing embolization require:
Role of the Radiology Research Center in Cerebral Aneurysm Research and Endovascular Innovation
The Radiology Research Center of Iran has been a leading institution in advanced neurovascular imaging and interventional radiology research. With a multidisciplinary team of neuroradiologists, neurosurgeons, physicists, and biomedical scientists, the center has contributed significantly to understanding and treating cerebral aneurysms through:
-
Clinical outcome studies comparing coiling versus surgical clipping
-
Research on prognostic factors and management strategies for unruptured aneurysms
-
Implementation of flow-diverter stent technologies for complex aneurysms
-
Development of advanced MRI and DSA imaging protocols
-
Integration of AI and image processing techniques for automated aneurysm detection
Future Research Directions
Current ongoing projects at the center include:
-
A national clinical trial evaluating dual balloon + stent-assisted coiling for challenging aneurysms
-
Application of machine learning models to predict rupture risk in asymptomatic aneurysms
-
Investigations into blood biomarkers for early aneurysm detection
These initiatives highlight the center’s commitment to combining clinical expertise with research innovation to improve neurovascular patient care.
The Radiology Research Center has published numerous articles in reputable national and international scientific journals. Some of the notable titles include:







Send to friends