A systematic review and meta analysis on the association between lymphocyte subsets and the severity of COVID 19
Introduction: Prominent prognostic parameters that reflect the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) to adopt an appropriate therapeutic approach are not fully identified. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to explore the association between lymphocyte variation and disease severity in COVID-19 individuals.
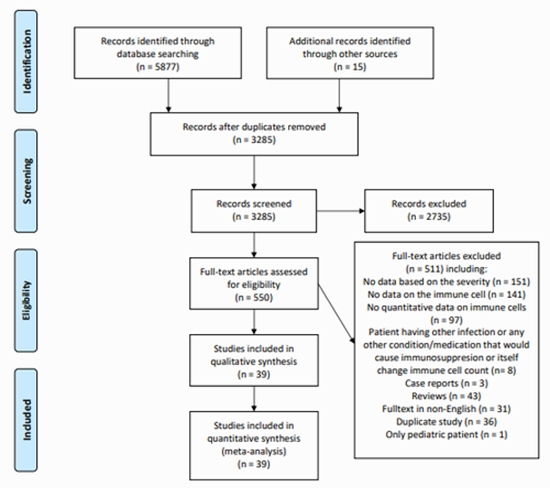
Methods: We searched Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, EMBASE and WHO website to retrieve studies investigating lymphocyte subset counts in non-severe and severe cases of COVID-19. The pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) between two groups and the pooled average count of each lymphocyte subset were assessed by employing a random-effect model.
Results: Thirty-nine investigations on 5087 participants, including 3578 non-severe patients and 1509 severe patients, were included. The pooled analysis showed that non-severe patients had higher total T lymphocytes (SMD = 1.01; 95% CI: 0.82, 1.20; I2 = 75.7%), T helper cells (SMD = 1.07; 95% CI: 0.85, 1.28; I2 = 85.4%), T cytotoxic cells (SMD = 1.07; 95% CI: 0.82, 1.32; I2 = 87.1%), B cells (SMD = 0.72; 95% CI: 0.45, 0.98; I2 = 79.7%), and natural killer cells (SMD = 0.65; 95% CI: 0.47, 0.84; I2 = 63.1%) than severe patients and the average count of the corresponding lymphocyte signatures in non-severe patients/severe patients were 878.88/448.40, 493.12/268.96, 311.91/158.91, 177.09/110.37, and 155.02/103.09 cells/μL, respectively.
Conclusion: Lymphopenia may be a dilemma in COVID-19 management because over-activation of lymphocytes may lead to cytokine storm or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In contrast, lymphopenia may increase SARS-CoV-2 amplification and COVID-19 severity. Therefore, novel therapies targeting lymphocyte proliferation or contraction may counterbalance lymphocyte counts in these patients.






comment