Immunogenicity of COVID 19 mRNA vaccines in immunocompromised patients: a systematic review and meta analysis
Background: Immunocompromised (IC) patients are at higher risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, morbidity, and mortality compared to the general population. They should be prioritized for primary prevention through vaccination. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in IC patients through a systematic review and meta-analysis approach.
Method: PubMed-MEDLINE, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched for original articles reporting the immunogenicity of two doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in adult patients with IC condition between June 1, 2020 and September 1, 2021. Meta-analysis was performed using either random or fixed effect according to the heterogeneity of the studies. Subgroup analysis was performed to identify potential sources of heterogeneity.
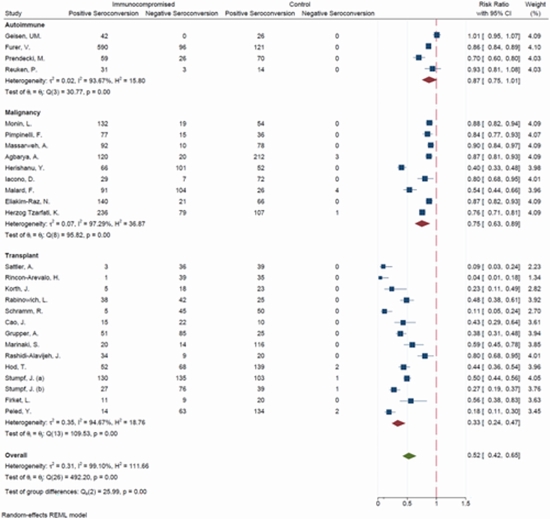
Results: A total of 26 studies on 3207 IC patients and 1726 healthy individuals were included. The risk of seroconversion in IC patients was 48% lower than those in controls (RR = 0.52 [0.42, 0.65]). IC patients with autoimmune conditions were 54%, and patients with malignancy were 42% more likely to have positive seroconversion than transplant recipients (P < 0.01). Subgroup meta-analysis based on the type of malignancy, revealed significantly higher proportion of positive seroconversion in solid organ compared to hematologic malignancies (RR = 0.88 [0.85, 0.92] vs. 0.61 [0.44, 0.86], P = 0.03). Subgroup meta-analysis based on type of transplantation (kidney vs. others) showed no statistically significant between-group difference of seroconversion (P = 0.55).
Conclusions: IC patients, especially transplant recipients, developed lower immunogenicity with two-dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. Among patients with IC, those with autoimmune conditions and solid organ malignancies are mostly benefited from COVID-19 vaccination. Findings from this meta-analysis could aid healthcare policymakers in making decisions regarding the importance of the booster dose or more strict personal protections in the IC patients.






comment