Complementary Role of Ultrasound in Management of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
To identify an effective method to identify high-risk patients for developing malignancy after molar evacuation
Background:
Transvaginal Ultrasonography is a noninvasive and inexpensive medical imaging tool used for the diagnosis of various diseases.
Objectives:
To identify an effective method to identify high-risk patients for developing malignancy after molar evacuation.
Patients and Methods:
A prospective serial assessment of 19 patients with gestational trophoblastic disease was performed. Clinical and laboratory data, transvaginal ultrasound and Doppler findings were evaluated the day before evacuation. They were followed-up in the first week after evacuation and every two weeks during the next two months, then every month until the sixth month.
Results:
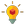
Ovarian theca lutein cysts (P = 0.018) (among pre-evacuation factors) and first week ultrasound (P = 0.02) can help in detecting high-risk patients. Even though, when β-hCG titer is not available in a high-risk patient, post evacuation myometrial involvement (P = 0.005) is a useful sign for detecting persistency.
Conclusions:
Some ultrasonographic features of molar pregnancy have capability to predict malignancy in the course of disease.




ارسال به دوستان