The performance of machine learning for predicting the recurrent stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis on 24,350 patients
Background: Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. Approximately one-third of patients with stroke experienced a second stroke. This study investigates the predictive value of machine learning (ML) algorithms for recurrent stroke.
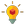
Method: This study was prepared according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline. PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science (WOS) were searched until January 1, 2024. The quality assessment of studies was conducted using the QUADAS-2 tool. The diagnostic meta-analysis was conducted to calculate the pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic accuracy, positive and negative diagnostic likelihood ratio (DLR), diagnostic accuracy, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and area under of the curve (AUC) by the MIDAS package in STATA V.17.
Results: Twelve studies, comprising 24,350 individuals, were included. The meta-analysis revealed a sensitivity of 71% (95% CI 0.64-0.78) and a specificity of 88% (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.76-0.95). Positive and negative DLR were 5.93 (95% CI 3.05-11.55) and 0.33 (95% CI 0.28-0.39), respectively. The diagnostic accuracy and DOR was 2.89 (95% CI 2.32-3.46) and 18.04 (95% CI 10.21-31.87), respectively. The summary ROC curve indicated an AUC of 0.82 (95% CI 0.78-0.85).
Conclusion: ML demonstrates promise in predicting recurrent strokes, with moderate to high sensitivity and specificity. However, the high heterogeneity observed underscores the need for standardized approaches and further research to enhance the reliability and generalizability of these models. ML-based recurrent stroke prediction can potentially augment clinical decision-making and improve patient outcomes by identifying high-risk patients.




ارسال نظر