بررسی حساسیت و اختصاصیت ترکیب دو روش (MRS) و DWI در درجه بندی تومورهای گلیال
در مطالعه حاضر کلیه بیماران مراجعه کننده به درمانگاه جراحی اعصاب با تشخیص گلیوم مغزی بر اساس نظر نورورادیولوژیست مجرب با توجه به کلیشه MRI که کاندید جراحی هستند تحت بررسی قرار گرفتند. بیماران با تومورهای گلیال اینفراتنتوریال که امکان مطالعه دقیق انها بکمک MRS و DWI کمتر فراهم است , انهایی که قبل از انجام مطالعه تحت مداخله درمانی ماژور قرار گرفته اند و از طرفی بیمارانی که با فاصله بیش از 1 ماه از زمان انجام مطالعه تحت جراحی قرار گرفته اند , از مطالعه خارج شدند. تومورهای مورد مطالعه براساس یافته های MRS و DWI و پاتولوژی پس از جراحی به دو دسته با درجه پاتولوژیک بالا (3 و 4 ) و پایین (1 و2 ) جهت سهولت مطالعه تقسیم شدند. بیماران پس از اخذ رضایت اگاهانه بکمک دستگاه MRI 3 تسلا تحت بررسی مشخصات متابولیک و ساختاری با استفاده از MRS و Diffusion MRI قرار گرفتند.
زمینه:
تشخیص تمایز بین گلیوماهای با درجه پایین و بالا میتواند در برنامهریزی درمانی بهینه و پیشآگهی مؤثر باشد. در مطالعات مختلف از تصویربرداری با انتشار (DWI) و امآر اسپکتروسکوپی (MRS) برای درجهبندی غیرتهاجمی گلیوما استفاده شده است، اما هر کدام تنها بر جنبههای محدودی تمرکز داشتهاند و با طراحیهای متفاوت انجام شدهاند که گاه نتایج ناسازگار و غیرقابل مقایسهای را در ادبیات علمی ایجاد کرده است.
اهداف:
این مطالعه با هدف معرفی بهترین پروتکل تصویربرداری و معتبرترین و کاربردیترین پارامترهای تصویربرداری در درجهبندی گلیوما با استفاده از DWI و MRS طراحی شد.
مواد و روشها:
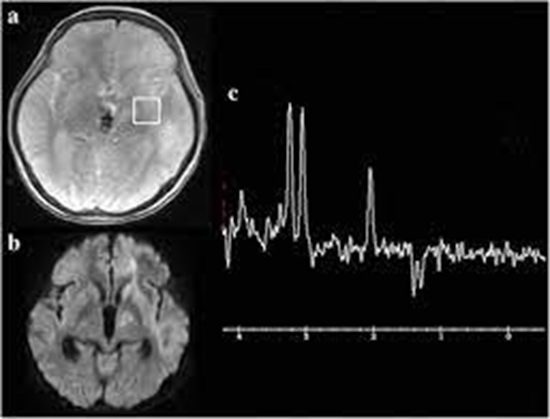
۵۵ بیمار مبتلا به گلیوما در این مطالعه آیندهنگر با دستگاه 3T-MR تحت MRS مغزی با زمانهای اکو کوتاه، متوسط و بلند و نیز DWI با b-value پایین، متوسط و بالا قرار گرفتند. پس از جراحی، تمام نمونهها بهطور آسیبشناسی با میکروسکوپ نوری درجهبندی شدند.
یافتهها:
نسبت Max(Chol/Cr)/Min(NAA/Cr) و پس از آن Max(Chol/Cr) (هر دو در زمان اکو بلند) معتبرترین نسبتهای متابولیتی در MRS برای درجهبندی دقیق گلیوما بودند، بهترتیب با AUC برابر 0.92 (p<0.05) و 0.89 (p=0.001)، در مقایسه با MRI متداول (cMRI) با AUC برابر 0.83 (p<0.05). دقت حداکثری DWI نشاندهنده AUC برابر 0.80 (p<0.05) بود.
نتیجهگیری:
نسبت Max(Chol/Cr)/Min(NAA/Cr) در زمان اکو بلند، معتبرترین پارامتر MRS در درجهبندی گلیوما شناخته شد. در حالیکه DWI نسبت به MRI متداول برتری نداشت. همچنین تفاوت معناداری میان b-valueهای مختلف یا بین مقادیر حداقل و میانگین ADC تومور در درجهبندی گلیوما بر اساس DWI مشاهده نشد.




ارسال نظر