Role of chest CT scan in patients with preexisting cancer and COVID 19 pneumonia
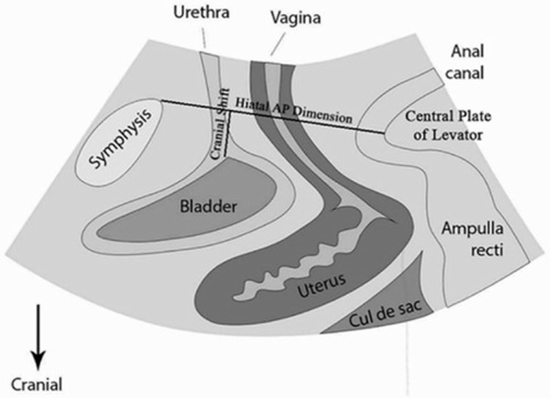
Purpose: To compare the correlation between 2D transperineal ultrasonography and physical examination (intravaginal palpation) for assessing pelvic floor and levator ani function.
Methods: Due to symptoms of pelvic floor disorder, 40 women between the ages of 29 and 75 were enrolled in this study as candidates for urodynamic and structural evaluation of the pelvic floor. A pelvic floor gynaecologist and radiologist assessed the levator ani function via physical examination (graded based on the Oxford Grading System) and transperineal 2D ultrasound, respectively.
Results: The ultrasound parameters for calculating the Levator Ani Index (LAI) demonstrate a difference between the anteroposterior dimension of the levator hiatus (r = 0.691, p < 0.001) and the cranial shift of muscle (r = 0.499, p < 0.001) at rest and during a squeezing manoeuvre in the mid-sagittal plane. Reduced anteroposterior diameter of the hiatus and increased cranial shift were associated with a higher Oxford Physical Examination Score (OPES). The association between LAI and OPES was independent of baseline variables such as age, BMI, number of births, and the presence of incontinence symptoms.
Conclusion: Measures such as the LAI can be used to quantify the function of the levator ani muscle, which may be useful for evaluating the efficacy of pelvic floor physiotherapy and exercise.




ارسال نظر