Systematic bone infection detection in axial diabetic foot MRI (Conference Paper)
This paper presents a system for detecting the toe bones in axial diabetic foot MRI and categorizing them
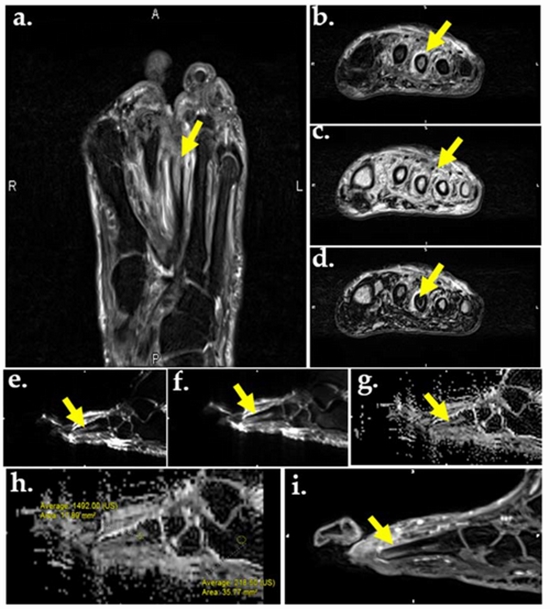
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that leads to tissue destruction and often to debility. Early diagnosis of infection is critical, as prompt antibiotic treatment reduces the rate of amputation. Vascular insufficiency and lack of sensation predispose diabetic patients to foot infection that can lead to bone infection. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has been shown to be capable of revealing primary marrow abnormalities with improved specificity comparing to other imaging options [1]. There will be an inevitable degree of variability in image interpretation as long as it relies on human visual perception. Therefore, tools that automate pattern recognition and image analysis can support clinical decision-making and may reduce this variability. The proposed system can be used as a basis for the computer-assisted radiology of diabetic foot infection. This paper presents a system for detecting the toe bones in axial diabetic foot MRI and categorizing them. The first aim of the system is to detect the toe bones using segmentation and filtering criteria. Detecting criteria are selected based on the experience of previous diagnoses and medical research in the area. Afterwards, the bag of feature approach is used to categorize the detected toe bones as infected, not infected or noise. For this purpose, we construct the visual vocabulary by clustering features that are extracted from a set of training images and use them to train multiclass linear support vector machine classifier for each of the three categories




ارسال به دوستان